24 Jan


Hello,
In this article, we are going to learn more about the TFT LCD technology and its interfacing with the Arduino board.
Hardware Required
Software Required
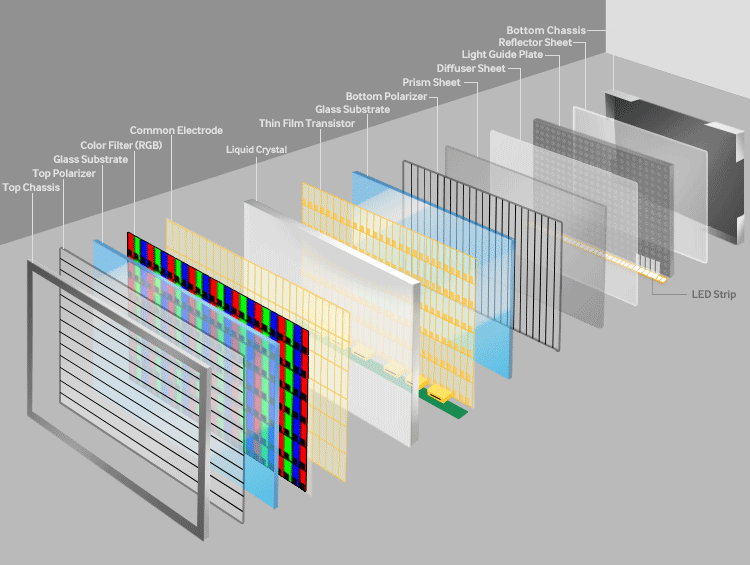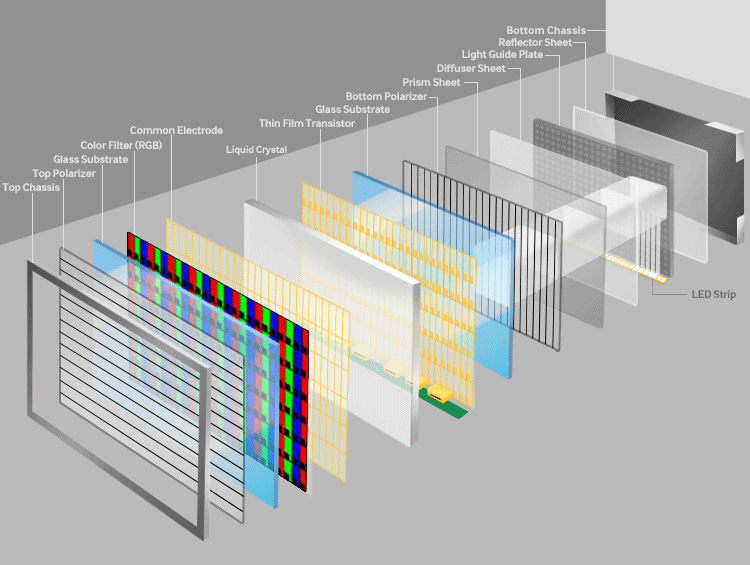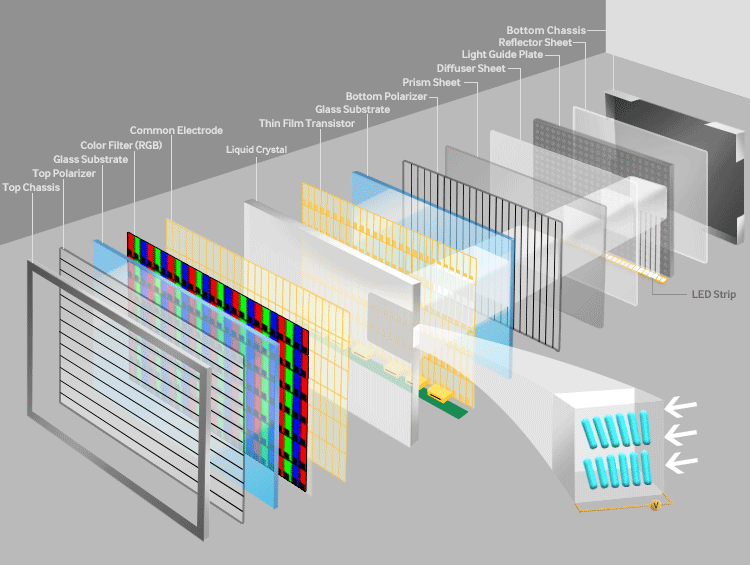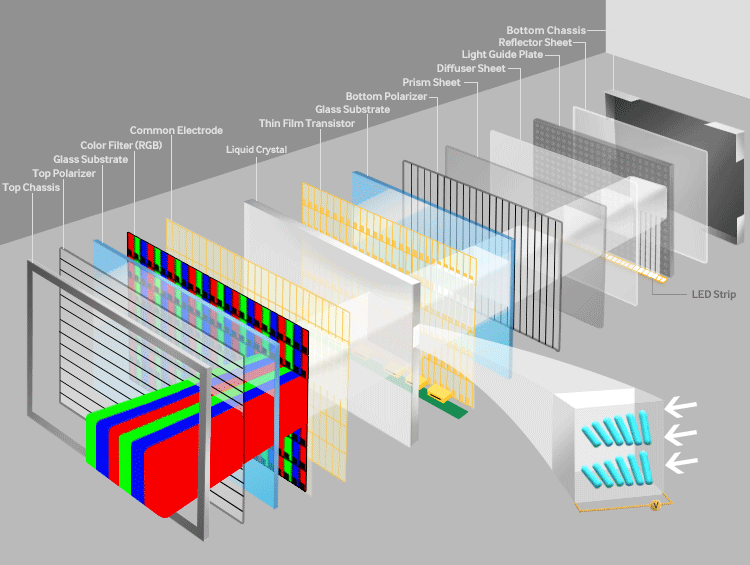
- The thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal-display is a type of LCD that uses thin-film-transistor technology. These kinds of displays are comprised of pixels, which are arranged vertically and horizontally. Pixels in the horizontal and vertical alignment make up the resolution of a display. For instance, if the resolution of a display is 1920x1080, then this means that it has 1920 pixels aligned horizontally and 1080 pixels aligned vertically. Every pixel has 3 sub-pixels which are colored RED, GREEN & BLUE. The question arises that how does an LCD generate all these colors. This question will be answered once we understand how the LCD works.
- There are four parts to understand if we want to understand how an LCD works.
Polarization layer
- I am sure many of you have heard the term polarization. The polarizing layer only allows the light to pass from one direction. This direction is the same direction in which the layer is tilted. In the TFT LCD, there are many layers. All of these layers are sandwiched between the two polarizing layers. Both the layers are transverse to each other, i.e. at 90 degrees from each other. So this alignment would mean that no light would pass through these two filters. How the light passes through these filters can be understood once we see how liquid crystals work.
Liquid Crystal
- Liquid crystals are generally oriented in random patterns. When squeezed between horizontal edged and vertical edged glasses, these crystals bend in a very predictable pattern. So now the light which is of horizontal orientation passes vertically through the liquid crystal. This liquid crystal is coated with a transparent electrode so when a voltage is passed through it, the liquid crystals align themselves accordingly.
Thin-film-transistor
- The thin-film layer decides the refresh rate of the display.
RGB Colour filter
- When the thin-film transistor is turned on, the liquid crystals do not twist the light beam and rather stop at vertical polarization. In this way, by adjusting the voltage, we can regulate the amount of light reaching the color filter. The brightness of each pixel will determine the color which will de be displayed. This way, by determining the voltage on each pixel, we can produce different types of colors.
Below is an animation made by Samsung to show how a TFT LCD Display works.
Different types of displays
- As we know, there are various technologies these days when it comes to displays like OLED, LCD, TFT, etc. We are going to compare them based on various attributes like brightness, contrast, view angle, power consumption, and resolution.
Interfacing with Arduino
- For interfacing the TFT display with the Arduino, we are using an Arduino shield.
- Place the shield on the Arduino Uno board making sure that all the pins are connected correctly.
Arduino Code
- First, you need to download and install the "SPFD5408" library. You can either download it here or in the manage libraries section in the Arduino IDE.
- After downloading the library, you need to install it inside Arduino IDE.
#include
#include
#define LCD_CS A3
#define LCD_CD A2
#define LCD_WR A1
#define LCD_RD A0
#define LCD_RESET A4
#define BLACK 0x0000
#define BLUE 0x001F
#define RED 0xF800
#define GREEN 0x07E0
#define CYAN 0x07FF
#define MAGENTA 0xF81F
#define YELLOW 0xFFE0
#define WHITE 0xFFFF
TftSpfd5408 tft(LCD_CS, LCD_CD, LCD_WR, LCD_RD, LCD_RESET);
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println(F("TFT LCD test"));
#ifdef USE_ADAFRUIT_SHIELD_PINOUT
Serial.println(F("Using Adafruit 2.8\" TFT Arduino Shield Pinout"));
#else
Serial.println(F("Using Adafruit 2.8\" TFT Breakout Board Pinout"));
#endif
Serial.print("TFT size is "); Serial.print(tft.width()); Serial.print("x"); Serial.println(tft.height());
tft.reset();
tft.begin(0x9341);
Serial.println(F("Benchmark Time (microseconds)"));
Serial.print(F("Screen fill "));
Serial.println(testFillScreen());
delay(500);
Serial.print(F("Text "));
Serial.println(testText());
delay(3000);
Serial.print(F("Lines "));
Serial.println(testLines(CYAN));
delay(500);
Serial.print(F("Horiz/Vert Lines "));
Serial.println(testFastLines(RED, BLUE));
delay(500);
Serial.print(F("Rectangles (outline) "));
Serial.println(testRects(GREEN));
delay(500);
Serial.print(F("Rectangles (filled) "));
Serial.println(testFilledRects(YELLOW, MAGENTA));
delay(500);
Serial.print(F("Circles (filled) "));
Serial.println(testFilledCircles(10, MAGENTA));
Serial.print(F("Circles (outline) "));
Serial.println(testCircles(10, WHITE));
delay(500);
Serial.print(F("Triangles (outline) "));
Serial.println(testTriangles());
delay(500);
Serial.print(F("Triangles (filled) "));
Serial.println(testFilledTriangles());
delay(500);
Serial.print(F("Rounded rects (outline) "));
Serial.println(testRoundRects());
delay(500);
Serial.print(F("Rounded rects (filled) "));
Serial.println(testFilledRoundRects());
delay(500);
Serial.println(F("Done!"));
}
void loop(void) {
for (uint8_t rotation = 0; rotation < 4; rotation++) {
tft.setRotation(rotation);
testText();
delay(2000);
}
}
unsigned long testFillScreen() {
unsigned long start = micros();
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
tft.fillScreen(RED);
tft.fillScreen(GREEN);
tft.fillScreen(BLUE);
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
return micros() - start;
}
unsigned long testText() {
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
unsigned long start = micros();
tft.setCursor(0, 0);
tft.setTextColor(WHITE); tft.setTextSize(1);
tft.println("Hello World!");
tft.setTextColor(YELLOW); tft.setTextSize(2);
tft.println(1234.56);
tft.setTextColor(RED); tft.setTextSize(3);
tft.println(0xDEADBEEF, HEX);
tft.println();
tft.setTextColor(GREEN);
tft.setTextSize(5);
tft.println("Groop");
tft.setTextSize(2);
tft.println("I implore thee,");
tft.setTextSize(1);
tft.println("my foonting turlingdromes.");
tft.println("And hooptiously drangle me");
tft.println("with crinkly bindlewurdles,");
tft.println("Or I will rend thee");
tft.println("in the gobberwarts");
tft.println("with my blurglecruncheon,");
tft.println("see if I don't!");
return micros() - start;
}
unsigned long testLines(uint16_t color) {
unsigned long start, t;
int x1, y1, x2, y2,
w = tft.width(),
h = tft.height();
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
x1 = y1 = 0;
y2 = h - 1;
start = micros();
for (x2 = 0; x2 < w; x2 += 6) tft.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, color);
x2 = w - 1;
for (y2 = 0; y2 < h; y2 += 6) tft.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, color);
t = micros() - start; // fillScreen doesn't count against timing
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
x1 = w - 1;
y1 = 0;
y2 = h - 1;
start = micros();
for (x2 = 0; x2 < w; x2 += 6) tft.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, color);
x2 = 0;
for (y2 = 0; y2 < h; y2 += 6) tft.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, color);
t += micros() - start;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
x1 = 0;
y1 = h - 1;
y2 = 0;
start = micros();
for (x2 = 0; x2 < w; x2 += 6) tft.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, color);
x2 = w - 1;
for (y2 = 0; y2 < h; y2 += 6) tft.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, color);
t += micros() - start;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
x1 = w - 1;
y1 = h - 1;
y2 = 0;
start = micros();
for (x2 = 0; x2 < w; x2 += 6) tft.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, color);
x2 = 0;
for (y2 = 0; y2 < h; y2 += 6) tft.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2, color);
return micros() - start;
}
unsigned long testFastLines(uint16_t color1, uint16_t color2) {
unsigned long start;
int x, y, w = tft.width(), h = tft.height();
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
start = micros();
for (y = 0; y < h; y += 5) tft.drawFastHLine(0, y, w, color1);
for (x = 0; x < w; x += 5) tft.drawFastVLine(x, 0, h, color2);
return micros() - start;
}
unsigned long testRects(uint16_t color) {
unsigned long start;
int n, i, i2,
cx = tft.width() / 2,
cy = tft.height() / 2;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
n = min(tft.width(), tft.height());
start = micros();
for (i = 2; i < n; i += 6) {
i2 = i / 2;
tft.drawRect(cx - i2, cy - i2, i, i, color);
}
return micros() - start;
}
unsigned long testFilledRects(uint16_t color1, uint16_t color2) {
unsigned long start, t = 0;
int n, i, i2,
cx = tft.width() / 2 - 1,
cy = tft.height() / 2 - 1;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
n = min(tft.width(), tft.height());
for (i = n; i > 0; i -= 6) {
i2 = i / 2;
start = micros();
tft.fillRect(cx - i2, cy - i2, i, i, color1);
t += micros() - start;
// Outlines are not included in timing results
tft.drawRect(cx - i2, cy - i2, i, i, color2);
}
return t;
}
unsigned long testFilledCircles(uint8_t radius, uint16_t color) {
unsigned long start;
int x, y, w = tft.width(), h = tft.height(), r2 = radius * 2;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
start = micros();
for (x = radius; x < w; x += r2) {
for (y = radius; y < h; y += r2) {
tft.fillCircle(x, y, radius, color);
}
}
return micros() - start;
}
unsigned long testCircles(uint8_t radius, uint16_t color) {
unsigned long start;
int x, y, r2 = radius * 2,
w = tft.width() + radius,
h = tft.height() + radius;
start = micros();
for (x = 0; x < w; x += r2) {
for (y = 0; y < h; y += r2) {
tft.drawCircle(x, y, radius, color);
}
}
return micros() - start;
}
unsigned long testTriangles() {
unsigned long start;
int n, i, cx = tft.width() / 2 - 1,
cy = tft.height() / 2 - 1;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
n = min(cx, cy);
start = micros();
for (i = 0; i < n; i += 5) {
tft.drawTriangle(
cx , cy - i, // peak
cx - i, cy + i, // bottom left
cx + i, cy + i, // bottom right
tft.color565(0, 0, i));
}
return micros() - start;
}
unsigned long testFilledTriangles() {
unsigned long start, t = 0;
int i, cx = tft.width() / 2 - 1,
cy = tft.height() / 2 - 1;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
start = micros();
for (i = min(cx, cy); i > 10; i -= 5) {
start = micros();
tft.fillTriangle(cx, cy - i, cx - i, cy + i, cx + i, cy + i,
tft.color565(0, i, i));
t += micros() - start;
tft.drawTriangle(cx, cy - i, cx - i, cy + i, cx + i, cy + i,
tft.color565(i, i, 0));
}
return t;
}
unsigned long testRoundRects() {
unsigned long start;
int w, i, i2,
cx = tft.width() / 2 - 1,
cy = tft.height() / 2 - 1;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
w = min(tft.width(), tft.height());
start = micros();
for (i = 0; i < w; i += 6) {
i2 = i / 2;
tft.drawRoundRect(cx - i2, cy - i2, i, i, i / 8, tft.color565(i, 0, 0));
}
return micros() - start;
}
unsigned long testFilledRoundRects() {
unsigned long start;
int i, i2,
cx = tft.width() / 2 - 1,
cy = tft.height() / 2 - 1;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
start = micros();
for (i = min(tft.width(), tft.height()); i > 20; i -= 6) {
i2 = i / 2;
tft.fillRoundRect(cx - i2, cy - i2, i, i, i / 8, tft.color565(0, i, 0));
}
return micros() - start;
}
- Upload this code to your Arduino board. It is a test code and can also be found under examples inside the Arduino IDE.
- I hope you're learned a lot about TFT displays through this article and I hope you liked it. Thank you.








Leave a Comment