Relays act as switches to regulate electrical circuits, making them crucial parts of automation and electronics. They fall into two primary categories: Solid-State Relays (SSR) and Mechanical Relays. We'll look at the variations between basic mechanical relays and SSR relay modules in this blog post.
Simple Relays
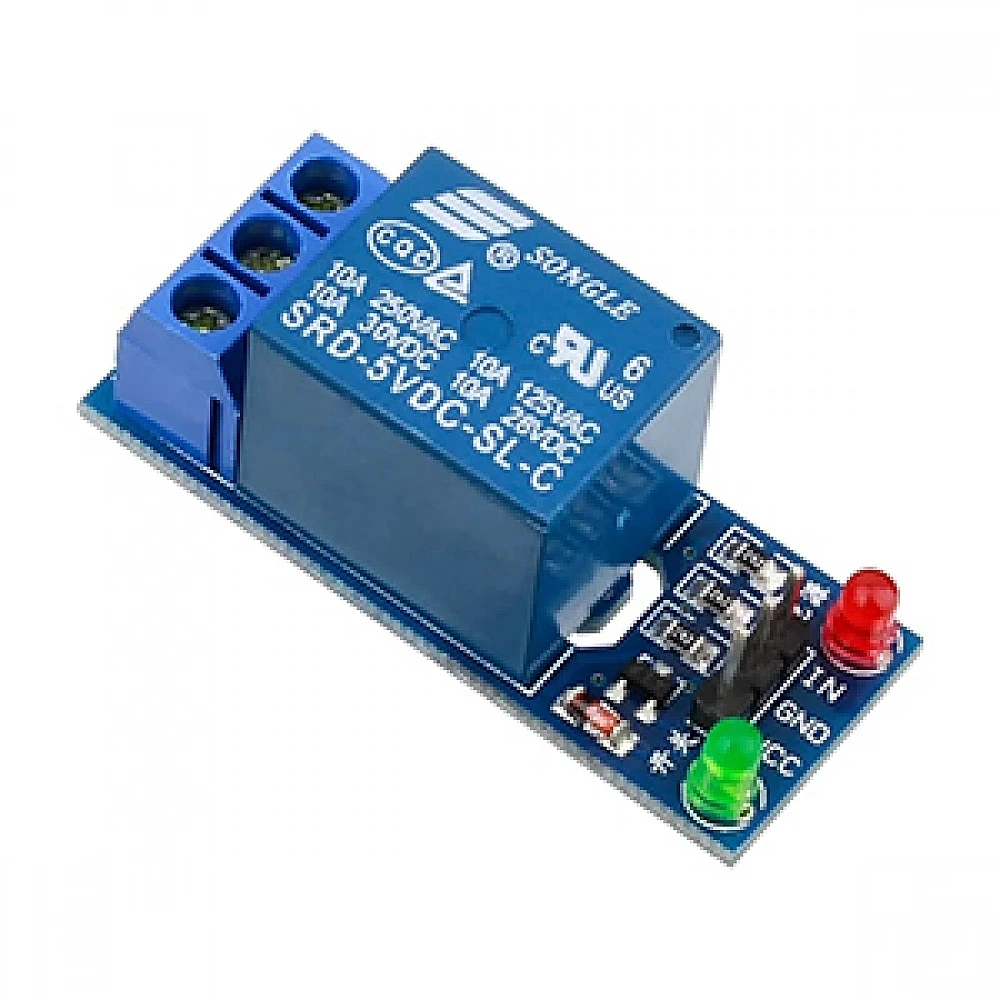

Mechanical Relays, often referred to as simple relays, are electromagnetic switches that use a coil to control the position of a set of contacts. Here's how they work:
-
Electromagnetic Coil: When you apply a current to the coil, it generates a magnetic field, which attracts an armature (a movable iron piece) towards it.
-
Contacts: As the armature moves, it physically connects or disconnects electrical contacts. This action completes or interrupts the circuit.
-
Advantages:
- Reliable for switching various loads, including high voltage and current.
- Easy to understand and widely available.
-
Limitations:
- Mechanical wear and tear over time.
- Relatively slow switching speed.
- Audible clicking sound during operation.
- Potential for contact arcing, which can lead to sparks and reduced lifespan.
Simple relays are commonly used in applications where switching speed is not critical, such as industrial control systems and traditional automation.
Solid-State Relay (SSR) Modules
Solid-State Relays (SSRs), on the other hand, are electronic switches that use semiconductor devices like thyristors, triacs, or transistors to perform the switching. Here's how they work:
-
Semiconductor Switching: Instead of physical contacts, SSRs use semiconductor components to switch the load. These components are turned on and off electronically.
-
Advantages:
- Silent operation with no audible clicking.
- Faster switching speed.
- No mechanical wear and tear, resulting in a longer lifespan.
- Lower power consumption.
-
Limitations:
- Limited to certain types of loads (resistive or inductive, depending on the SSR).
- May require heat sinks for dissipating heat generated during switching.
SSR relay modules are well-suited for applications where rapid and silent switching is crucial, and they are often used in areas like industrial automation, robotics, and precise temperature control systems.
Key Differences
The primary differences between SSR relay modules and simple relays can be summarized as follows:
-
Switching Mechanism: Simple relays use mechanical switches, while SSRs use semiconductor devices for switching.
-
Speed: SSRs switch faster and with no audible noise, making them ideal for applications that require rapid and silent operation.
-
Wear and Tear: Simple relays have moving parts and are subject to mechanical wear, while SSRs have no moving parts and, therefore, have a longer lifespan.
-
Applications: Simple relays are versatile and can handle various types of loads, whereas SSRs are more specialized and suitable for specific applications.
In conclusion, the requirements of your particular application will determine whether to use SSR relay modules or simple relays. SSRs are frequently the recommended option if you require quick, silent, and dependable switching, particularly in electronic or highly automated systems. Simple relays, on the other hand, can be an affordable option for more general-purpose applications or situations where mechanical switching is acceptable.




Leave a Comment